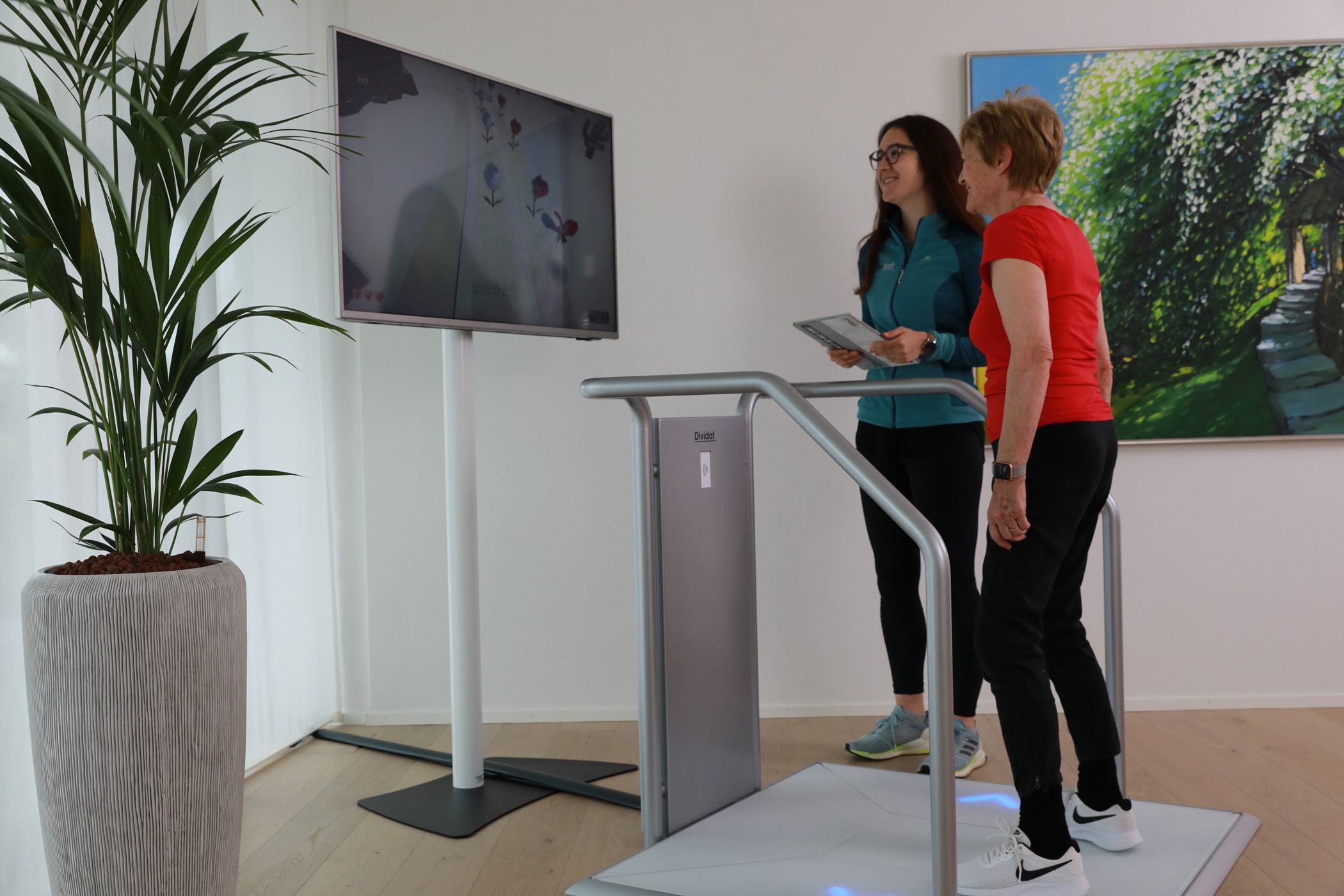
news
Adaptations of Prefrontal Brain Activity, Executive Functions, and Gait in Healthy Elderly Following Exergame and Balance Training: A Randomized-Controlled Study
You can download the study overview and the full study here:
Background
The aim of this study was to compare conventional balance training with video game-based physical exercise, a so-called exergame, on the relative power (RP) of electroencephalographic (EEG) frequencies over the PFC, executive function (EF), and gait performance. To improve motor and cognitive performance in elderly, it can be hypothesized that a physical training that also targets executive functions* (EFs) might be an important component.
The study was a randomized controlled trial (RCT) including two parallel running intervention groups. All participants completed 24 trainings including three times a 30 min session/week.
*Executive Function (EF) can be defined as “the management system of the brain.” According to WebMD, "executive functioning skills help you get things done." There are three main areas of Executive Function (EF):
Exergame Group
Played four different games developed and provided by Dividat.
The games specifically train EFs that are associated with the prefrontal brain area.
Each game included different difficulty levels to ensure adaption and progression to the abilities of each individual.
Balance Group
Trained with conventional balance training.
Participants performed repetitive static and dynamic exercises on stable and unstable surfaces to challenge their balance.
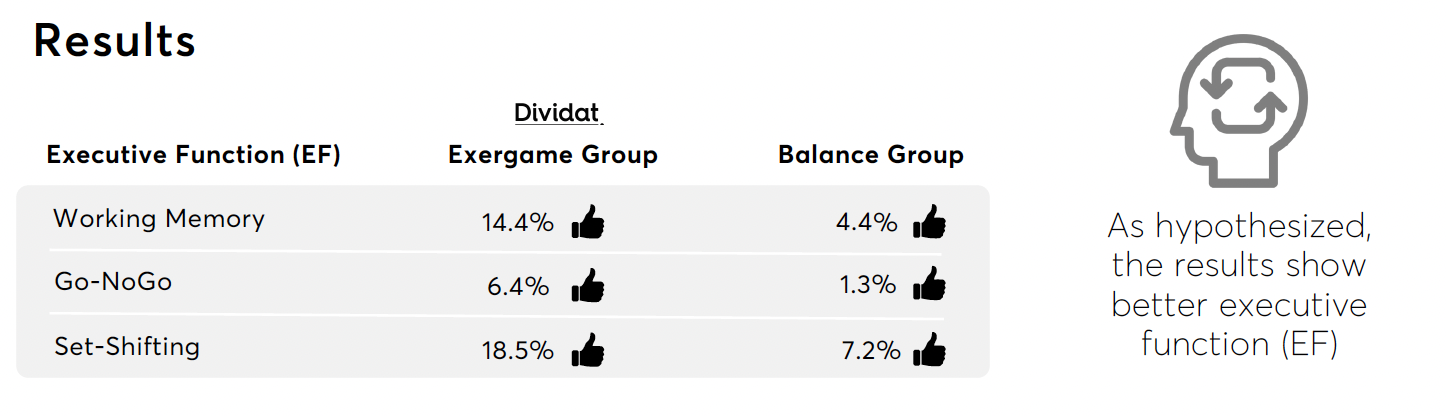
Results
Conclusion and Outlook
The results indicate that exergame training as well as balance training positively influence prefrontal cortex activity and/or function in varying proportion. The present study illustrated that especially exergame training affects prefrontal theta RP and that exergame training and balance training positively influence EF.
Two recent reviews, focusing on the interplay between physical function and cognition, concluded that it seems important to combine motor and cognitive exercises into clinical practice to enable older adults to move safer in their physical environment.
